|
|
|
|
A numerical tour of wave propagation |
Note that all sub-equations can be formulated in the following form:
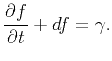 |
(49) |
The analytic solution of this equation is
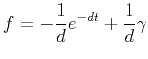 |
(50) |
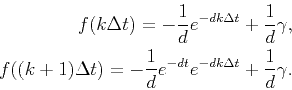 |
(51) |
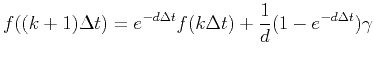 |
(52) |
For
![]() ,
,
![]() , the update rule becomes
, the update rule becomes
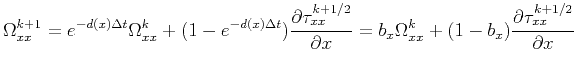 |
(53) |
As can be seen from Eq. (27), we only need to subtract the reflection part ![]() and
and ![]() after global updating (Eq. (9)). We summarize this precedure as follows:
after global updating (Eq. (9)). We summarize this precedure as follows:
Step 1: Perform the computation of Eq. (9) in whole area;
Step 2: In PML zone, subtract decaying parts according to Eq. (27).
|
|
|
|
A numerical tour of wave propagation |