Next: Downloading and Installing IWAVE
Up: Using IWAVE
Previous: Bibliography
All IWAVE applications are parameter-driven: that is, they accept as
input a map or associative array, defined by
a list of key = value pairs. These parameter specifications can
be included on the command line. However, because the number of such
parameter specifications is rather large, it's convenient to store
them in a parameter file (``par file''). The use of a par file has the
added advantage that the file may include annotations and white space to
improve readability.
The examples displayed in this paper are created in the directory $TOP/demo/data. The par file parfile is a by-product of data
creation - the SConstruct script text-processes it from prototype
files including macros, which are resolved when the scripts are
run. Four such prototype par files are present in data, each one defining
a modeling task corresponding to a given level of grid refinement.
The actual input to the modeling command is parfile.
The meaning of each parameter in the par file is described in the IWAVE
web documentation (Terentyev et al., 2012).
This appendix gives a brief description of the parameter assignments
appearing in the parfile generated for the 20 m grid example. To
run this example, and coincidentally generate its parameter file,
- cd $TOP/demo/data
- scons demo20m
The file parfile groups job parameters into blocks. The first
block looks like this:
INPUT DATA FOR iwave
------------------------------------------------------------------------
FD:
order = 2 spatial half-order
cfl = 0.4 proportion of max dt/dx
cmin = 1.0
cmax = 4.5
dmin = 0.5
dmax = 5.0
fpeak = 0.010 central frequency
Note that comments, block labels, and typographical separators are all
accommodated. The IWAVE parameter parser identifies parameter
specifications by strings of the form
key = value
consisting of a string with no embedded whitespace, followed by an
= sign surrounded by any amount of whitespace on either side,
followed by another string with no embedded whitespace. Strings with embedded
whitespace are also allowed, provided that they are double-quoted -
thus "this is a value" is a legitimate value expression. Other
capabilities of the parser are described in its html
documentation. All values are first read as strings, then
converted to other types as required.
The parameters appearing in parfile are as follows:
- order = 2: half-order of the spatial difference scheme -
asg implements schemes of order 2 in time, and 2k in space,
for certain values of k, the spatial half-order, which is the value
associated to the key order. Permissible values
of order in the current release are 1, 2, and 4.
- cfl = 0.4: max time step is computed using one osf several
criteria - see html docs for details. This number is the fraction of
the max step used. Must lie between 0.0 and 1.0.
- cmin, cmax, dmin, dmax: sanity checks on density and
velocity values. The max permitted velocity cmax also figures
in two of the max time step criteria. Violation of these bounds
causes an informative error message with traceback information to be
written to the output file cout[rk].txt, where rk is the
MPI global rank ( = 0 for serial execution), and the program to
exit. IWAVE handles all trappable fatal errors in this way.
- fpeak = 0.010: nominal central frequency, in kHz. Used in
two ways: (1) to set the width of absorbing boundary layers by
defining a wavelength at max velocity cmax, and (2) as the
center frequency of a Ricker wavelet in case the point source Ricker
option is chosen for source generation. Plays no other role.
- nl1, nr1, nl2, nr2: specify 2D PML layer thicknesses: nl1 describes the layer thickness, in wavelengths determined as
described in the preceding bullet, of the left boundary (with
lesser coordinate) in the axis 1 direction, etc. Set = 0.0 for no
layer, in which case the free (pressure-release) boundary condition
is applied.
- srctype = point: this application implements two source
representations, a point source with amplitude options and a very flexible array
source option.
- "source = ....": a quoted parameter spec is just a
string, from the IWAVE parser's point of view, so does not define
anything: this parameter is commented out. If it were not quoted, it
would define the pathname to an SU file containing source data -
either a wavelet (first trace) for point source, or an array source specified
by a number of traces (if srctype=array). If a source wavelet is not specified (as
it is not for the scripted examples), the application creates a Ricker wavelet of central
frequency fpeak.
- sampord = 0: order of spatial interpolation. Legal values
are 0 and 1. 0 signifies rounding down the source coordinates to the
nearest gridpoint with smaller coordinates. 1 signifies piecewise
multilinear interpolation (or adjoint interpolation, for the
source), so that a point source at
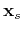 is
represented as a convex linear combination of point sources at
the corners of the grid cube in which
is
represented as a convex linear combination of point sources at
the corners of the grid cube in which 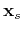 lies, and receiver values
are similar convex combinations of nearby grid function values. The first option is
appropriate for synthetic examples in which sources and receivers
lie on the grid. The second permits arbitrary placement of sources
and receivers, and is compatible with the overall second-order
accuracy of asg.
lies, and receiver values
are similar convex combinations of nearby grid function values. The first option is
appropriate for synthetic examples in which sources and receivers
lie on the grid. The second permits arbitrary placement of sources
and receivers, and is compatible with the overall second-order
accuracy of asg.
- refdist = 1000.0, refamp = 1.0: point source calibration
rule developed for the SEAM project - the wavelet is
adjusted to produce the pulse shape read from the file specified by
the source parameter, or a Ricker wavelet of central frequency
fpeak if the source parameter is not assigned a value,
with amplitude (in GPa) given by refamp at the
prescribed distance (in m) given by refdist, assuming a homogenous medium with
parameters the same as those at the source point, and absorbing
boundary conditions. If refdist is set to
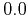 , then source
pulse (either read from a file, if source is set, or a Ricker
of peak frequency fpeak otherwise) is simply used as the time
function in the discrete point source radiator.
, then source
pulse (either read from a file, if source is set, or a Ricker
of peak frequency fpeak otherwise) is simply used as the time
function in the discrete point source radiator.
- hdrfile = ...: IWAVE specifies acquisition parameters
such as source and receiver locations, time sample rates and delays,
and so on, by supplying trace headers in a file: the traces produced
in simulation have the same headers. At present, the only
implemented option for specifying headers is via a path to an SU
file, that is, a SEGY-formatted file with reel header stripped
off. Other options are planned for future releases.
- datafile = ...: pathname for output data file; on normal
completion of run, contains traces with
same headers as in hdrfile, computed trace samples. Note that
sample rate of output traces is whatever is specified in hdrfile, and generally is not the same as the time step used in
the simulation, the trace samples being resampled on output. Note
also that pathnames may be either fully qualified (as in the hdrfile
entry) or relative.
- velocity = ..., density = ...: pathnames to rsf header
files for velocity and density. Other combinations of physical
parameters are admissible, such as bulk modulus and density, bulk
modulus and bouyancy (reciprocal density), velocity and
buoyancy. Data stored in RSF disk format, described in Madagascar
web documentation. Current proxy for unit conversions: scaling
during read/write by power of 10, given by scale keyword
(extension to standard RSF). Must be chosen so that output is in
m/ms or km/s for velocity, g/cm
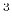 for density, or compatible units
for other parameters (eg. GPa for bulk modulus).
for density, or compatible units
for other parameters (eg. GPa for bulk modulus).
- mpi_np1 = ..., partask = 1: parallelism parameters - mpi_np1 gives the number of domains along axis 1, etc. (loop or
domain decomposition), and
partask gives the number of shots to load simultaneously
(task parallelization over shots). Domain decomposition and task
parallelization may be used alone or in combination. Setting the
value = 1 for all of these parameters signifies serial execution, even if the
code is compiled with MPI. To execute in parallel, compilation with
MPI is a precondition - see installation instructions.
- dump_pi = ...: dump parameters regulate verbosity, with
output being sent to text files cout0.txt (serial) or cout[rk].txt, rk = MPI global rank encoded with uniform field width for
parallel execution. Individual parameters described in the html
documentation. If all dump parameters are set to zero, asg is
silent, i.e. all cout... files will be empty on completion.
The parameters described here represent one common use case of IWAVE's
acoustic application. The web documentation describes a number of
other use cases.
Next: Downloading and Installing IWAVE
Up: Using IWAVE
Previous: Bibliography
2012-10-17